Issue :- 94
Diabetes

Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose from food get into your cells to be used for energy. Sometimes your body doesn’t make enough-or any-insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells.
What are the different types of diabetes?
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Gestational Diabetes
- Prediabetes
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. Your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
- Extreme Hunger
- Increased Thirst
- Unintentional Weight Loss
- Frequent Urination
- Blurry Vision
- Tiredness
- It May Also Result In Mood Changes
Type 2 diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make or use insulin well. You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes

Prediabetes
Prediabetes occurs when your blood sugar is higher than normal, but it’s not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
Most women with gestational diabetes don’t have any symptoms. The condition is often detected during a routine blood sugar test or oral glucose tolerance test that is usually performed between the 24th and 28th weeks of gestation. In rare cases, a woman with gestational diabetes will also experience increased thirst or urination.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination (from urinary tract infections or kidney problems)
- Weight loss or gain
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Nausea
- Skin infections
- Darkening of skin in areas of body creases
- Breath odor that is fruity, sweet, or an acetone odor
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet

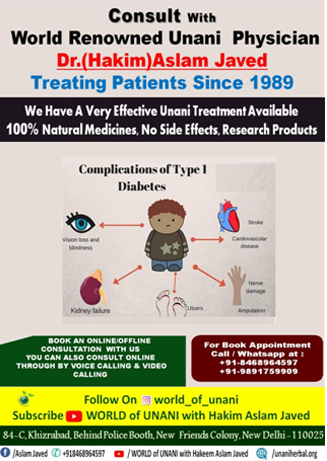
Diabetes complications
High blood sugar damages organs and tissues throughout your body. The higher your blood sugar is and the longer you live with it, the greater your risk for complications.
Complications associated with diabetes include:
- heart disease, heart attack, and stroke
- neuropathy
- nephropathy
- retinopathy and vision loss
- hearing loss
- foot damage such as infections and sores that don’t heal
- skin conditions such as bacterial and fungal infections
- depression
- dementia
Diabetes prevention
- Type 1 diabetes isn’t preventable because it’s caused by a problem with the immune system. Some causes of type 2 diabetes, such as your genes or age, aren’t under your control either.
- Yet many other diabetes risk factors are controllable. Most diabetes prevention strategies involve making simple adjustments to your diet and fitness routine.
- If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes, here are a few things you can do to delay or prevent type 2 diabetes:
- Get at least 150 minutes per week of aerobic exercise, such as walking or cycling.
- Cut saturated and trans fats, along with refined carbohydrates, out of your diet.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Eat smaller portions.
- Try to lose 7 percentTrusted Source of your body weight if you’re overweight or obese.
- These aren’t the only ways to prevent diabetes. Discover more strategies that may help you avoid this chronic disease.

Nomination form for 2020 Global Awards
https://www.unaniherbal.org/nomination-form.html
For Consultation click here
Copyright 2014 Unani Herbal
If you wish to cancel your subscription to this newsletter click here





